Tangential Acceleration Formula
In rotational motion, tangential acceleration is a measure of how quickly a tangential velocity changes. It always acts perpendicular to the centripetal acceleration of a rotating object. It is equal to the angular acceleration α, times the radius of the rotation.
tangential acceleration = (radius of the rotation)(angular acceleration)
atan = rα
atan = tangential acceleration
r = radius of the object's rotation
α = angular acceleration, with units radians/s2
Tangential Acceleration Formula Questions:
1) A car that has tires with radius 20.0 cm (0.200 m) begins to accelerate forward. The acceleration comes from the engine, which produces an angular acceleration of the tires α = 12.0 radians/s2. What is the tangential acceleration of the tires?
Answer: The tangential acceleration of the tires can be found from the formula:
atan = rα
atan = (0.200 m)(12.0 radians/s2)
atan = 2.40 m/s2
The tangential acceleration of the tires is 2.40 m/s2 (this is also the resulting acceleration of the car).
2) A child spins a toy top, applying a force to the peg in the middle. The force applied results in a tangential acceleration of the peg. If the radius of the peg is 0.50 cm (0.0050 m), and the tangential acceleration applied is atan = 0.540 m/s2, what is the angular acceleration of the top?
Answer: The angular acceleration can be found by rearranging the equation:
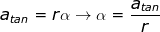
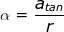
α = 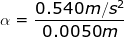
α = 108 radians/s2
The angular acceleration of the top is 108 radians/s2.
|
Related Links: |
